What Is The Lymph System?
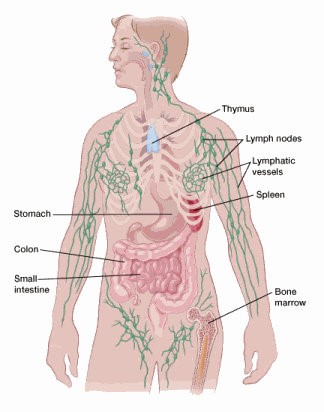
Lymph fluid circulates through the body and contains proteins, salts, and water, as well as white blood cells, which help fight infection.
Lymph vessels or ducts have one-way valves that work with body muscles to help move the fluid through the body and control the flow.
Lymph nodes are small, bean-sized glands along the lymph vessels that work to help filter foreign substances, such as tumor cells and infections. Lymph nodes are in many parts of the body, including the neck, armpit, chest, abdomen (belly), and groin.
The tonsils, adenoids, spleen, and thymus are also parts of the lymph system.
What Type Of White Blood Cells Are Found In The Lymph?
B cells – help protect against future infections from previously encountered germs by retaining information about a germ’s molecular signature
T cells – are produced in the bone marrow and travel to the thymus where they mature. T cells actively destroy infected cell and signal other immune cells to participate in the immune response.
NK cells – are lymphocytes that circulate in the blood in search of infected or diseased cells. When NK cells come across a tumor cell or a cell that is infected with a virus, they surround and destroy the diseased cell by releasing the chemical-containing granules.
Primary Organs Of The Lymphatic System
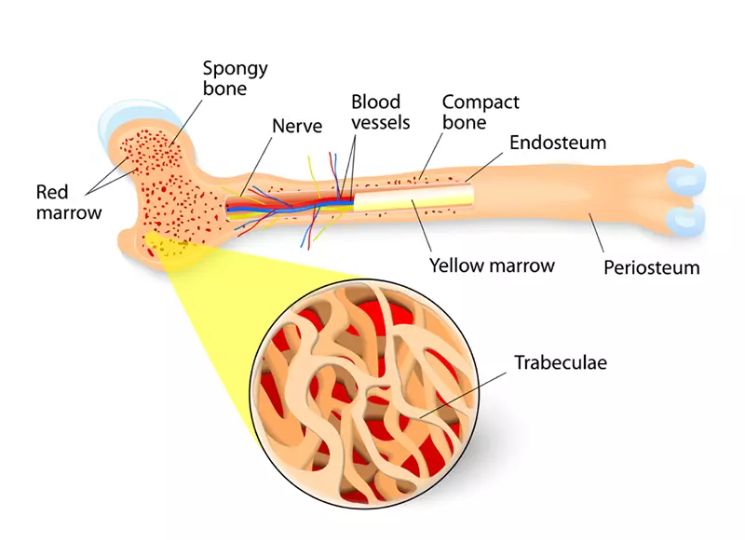
BONE
The main purpose of the bone marrow, a substance found inside bones, is to produce stem cells that will later differentiate into osteoblasts, which will make new bone and blood cells. These cells (red, white, and platelets) are made in the bone marrow and subsequently sent to secondary organs to mature. Additionally, it is in charge of the yellow bone marrow’s storage of fat.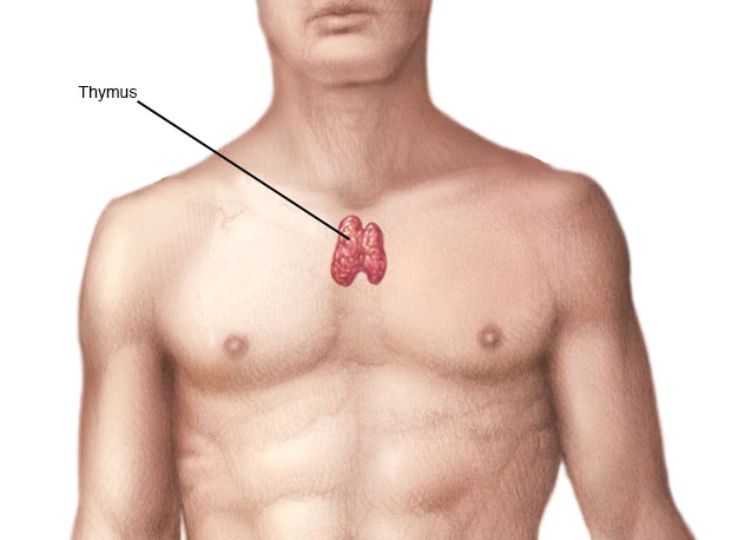
THYMUS GLAND
Another important lymphatic system organ is the Thymus Gland. Just below the upper sternum, it is situated in the upper chest. Its main job is to encourage the growth of immune system cells called T-lymphocytes or T-cells. These white blood cells defend the body against pathogens and foreign invaders. Once your T-cells are produced, they are directed to the lymph nodes and your spleen, where these cells move. They are in charge of warding off infections, germs, and viruses once there. Your body requires the antibodies that they produce to remain healthy.Secondary Organs Of The Lymphatic System
TONSIL
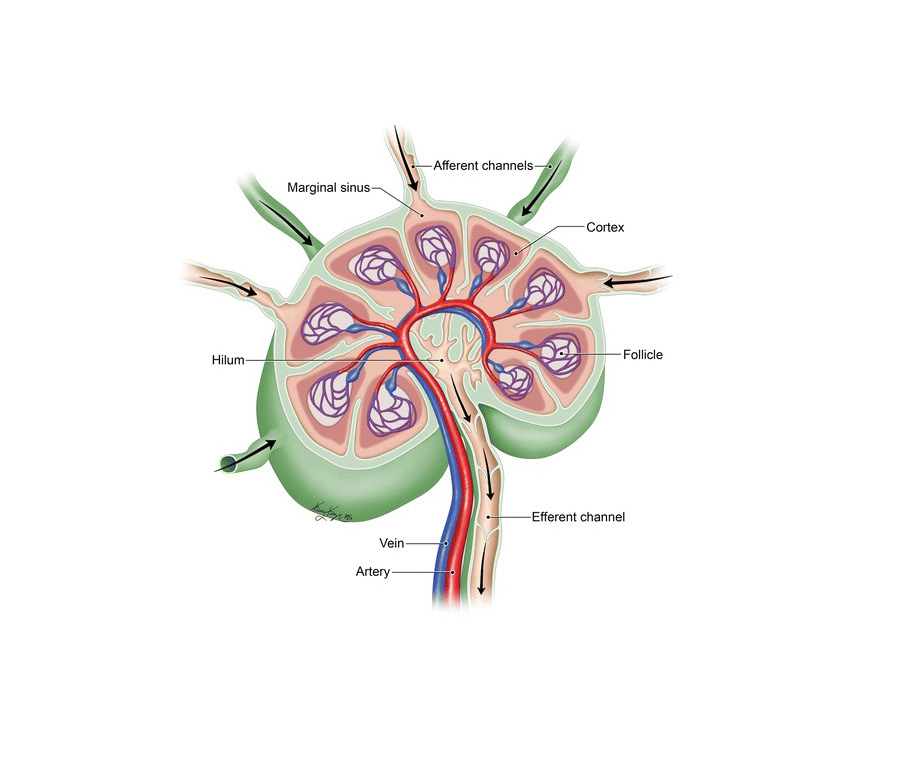
LYMPH NODES
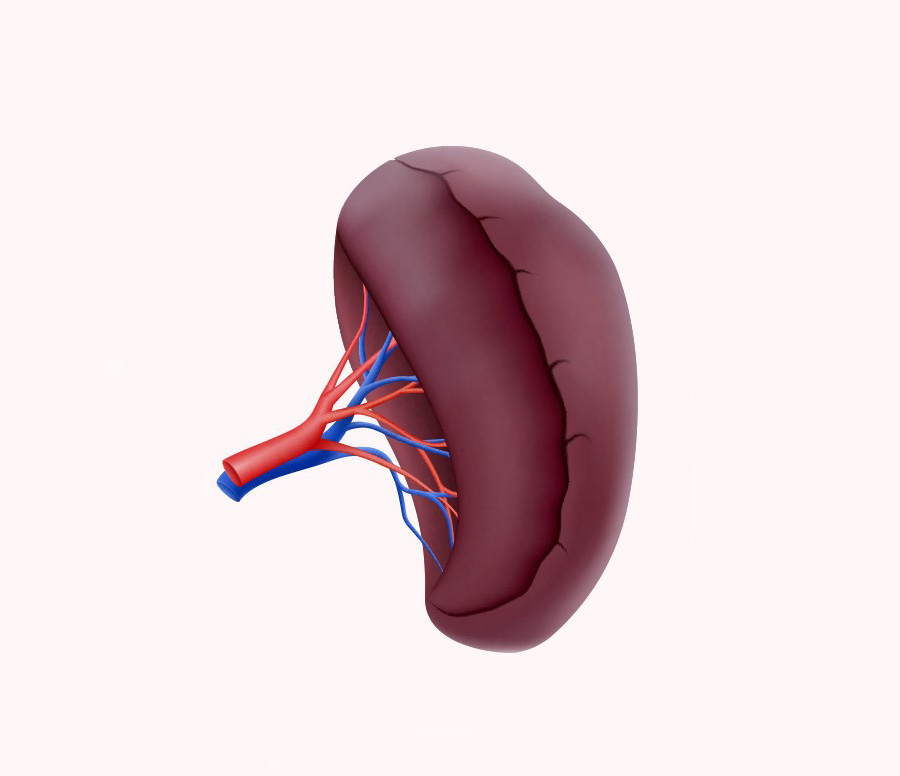
SPLEEN
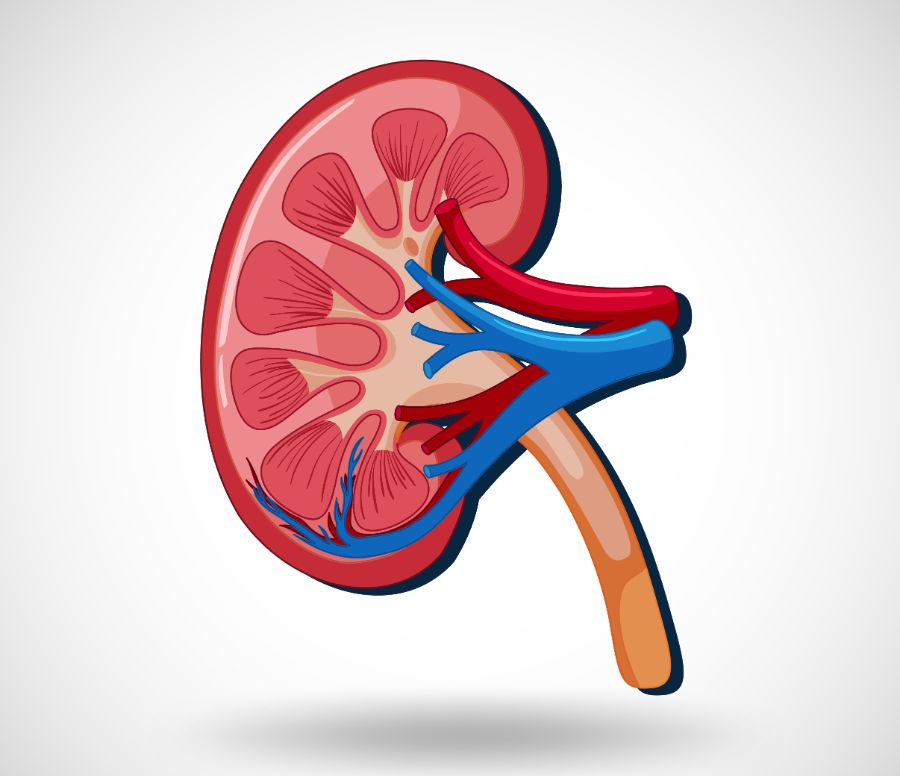
KIDNEY
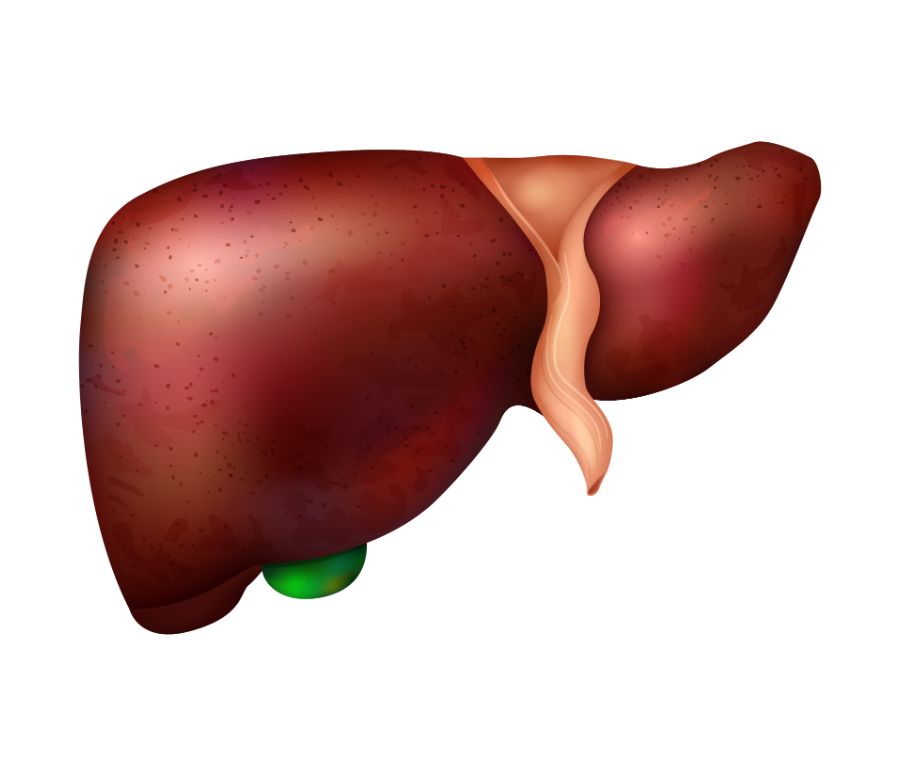
LIVER
Before it is distributed to the rest of the body, the liver’s primary function is to filter blood arriving from the digestive system. The liver also breaks down medications and detoxifies chemicals. The liver secretes bile while it works, which then travels back to the intestines. Additionally, the liver produces proteins necessary for blood coagulation and other processes. The lymphatic system is overworked if the liver isn’t working properly.
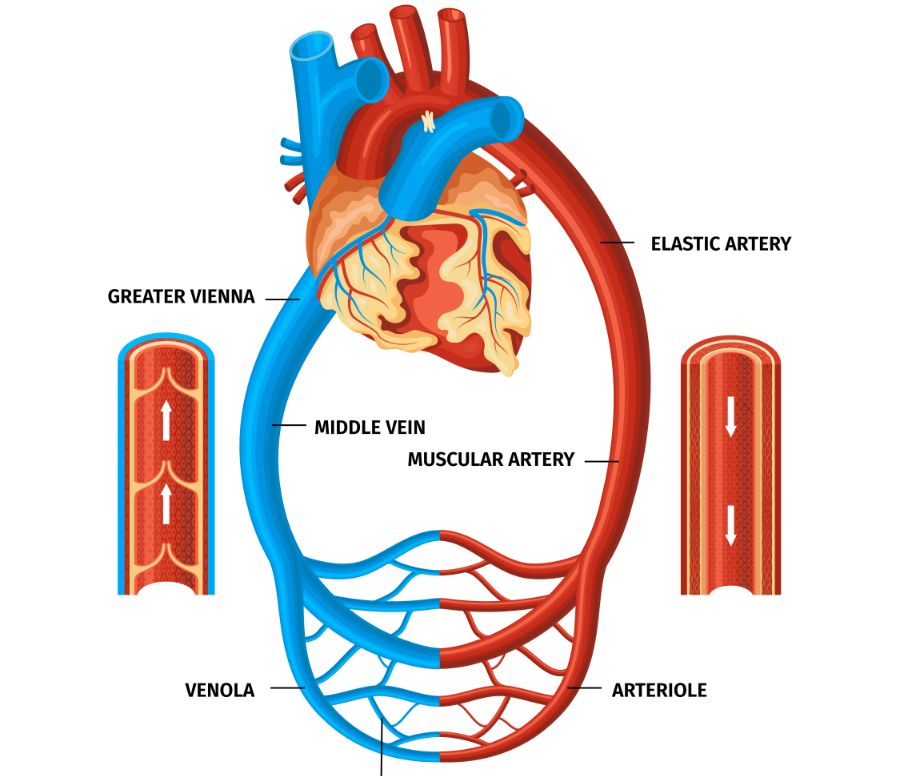
CARDIO-VASCULAR SYSTEM
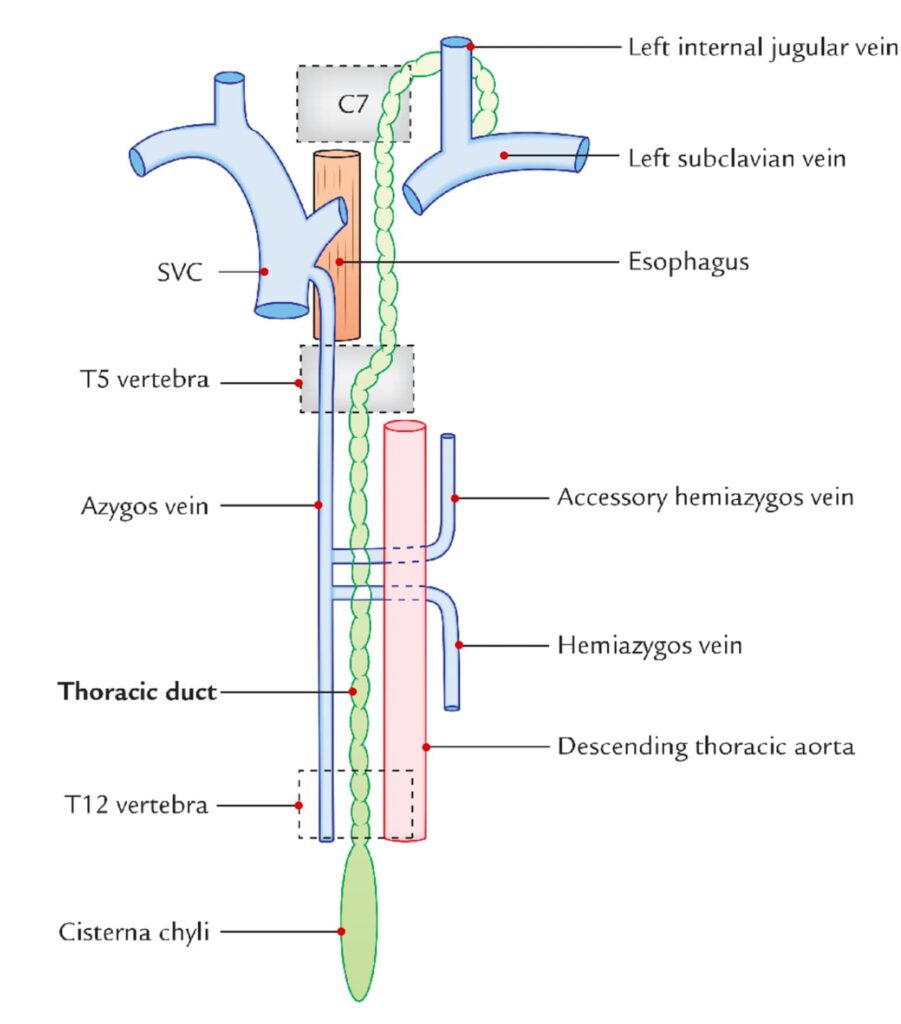
How Does The Lymph Move Into The Circulatory System?
• Originates in the abdomen at cisterna Chyli
• Transverses the Diaphragm
• Collects Lymph and emulsified fats
• Connects/collects lymph from the L arm, head and neck as well as the R thoracic duct
• It is responsible for transporting lymph into the circulatory system
• Transport of lymph here is caused by the
movement of breathing
• It transports 4 liters of lymph a day
What Causes Problems in the Lymphatic System?
The lymphatic system is a complex network of lymph vessels, lymph nodes, and lymphoid organs that play a vital role in maintaining fluid balance, immune function, and the absorption of fats and fat-soluble vitamins. Several factors can lead to problems with the lymphatic system one of these is Lymphedema.
What Is Lymphedema?
Lymphedema is a disorder of the lymphatic system that causes a person to develop swollen, heavy legs and arms. Lymphatic cancer, radiation therapy and breast cancer treatment are the most common causes of lymphedema. It is important for individuals suffering from this condition to manage it so that their quality of life does not get affected. There are standard treatments such as compression garments, self-massaging and draining that are effective in managing swelling, which can be costly at times. At the same time, there are ways to manage lymphedema more inexpensively by applying simple principles that can offer great relief.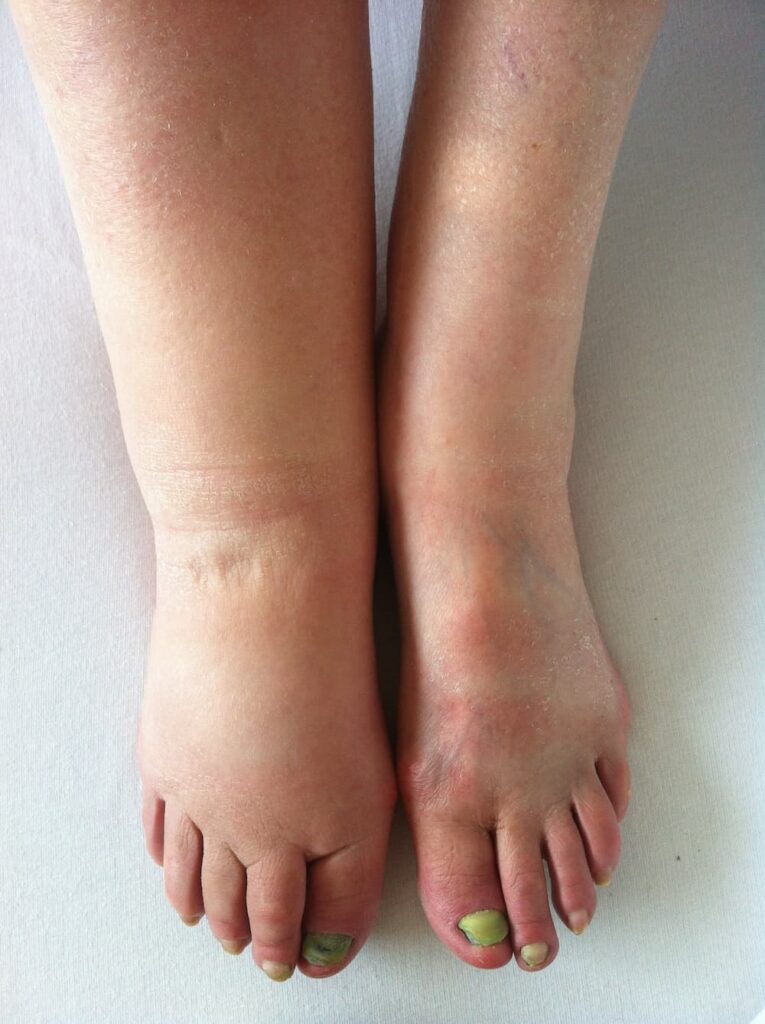
What Are The Causes Of Lymphedema?
In many cases, minor and/or major lymphatic vessels are disrupted by surgery, injury, radiotherapy or infection.
As a result of the damage to the lymphatic system, the remaining vessels are no longer capable of draining the fluid accumulating in tissue, and lymphedema develops.
The most common cause for secondary lymphedema in the Western world is cancer surgery involving removal and/or radiotherapy of the lymph nodes.
Any vascular surgery like vein ablation can cause secondary lymphedema as well.
Sometimes edema does not occur immediately after cancer treatment, but several months or even years later, despite the necessary precautions being taken; a medical specialist should be consulted in such cases to rule out the growth of any new tumors.
You Can Checkout This Video For More Info on Lymphedema
Symptoms Of Lymphedema
One of the common symptoms of lymphedema is swelling of the arm, leg, trunk or any body part. Swelling can stay only for a short time and it will disappear without any treatment then return again. When swelling comes and goes away, that might be the beginning of chronic lymphedema. Sooner you address lymphedema management, faster you will see results.
Some of the common symptoms are as follow:
- Heaviness on limbs
- Loss of flexibility in hand, wrist or ankle
- Pitting edema (Swelling in which imprint remains after light touch)
Treatments For Lymphedema
Compression Bandages and Garments: Helps to manage lymphedema. Compression bandages help to maintain lymphedema while you are using it.
Exercises: Exercises are very important to manage lymphedema, muscle contraction moves lymph fluid and helps to regulate fluid. Exercises have to be in the proper sequence to see the best result.
Skin Care : Proper skin care should be the routine for lymphedema patients, it’s easy to get dry skin and dry skin can lead to cellulitis so routine skin care helps to reduce risk of infection.
Healthy Diets: Healthy weight helps to reduce risk of lymphedema, there is no specific diet that you have to follow but managing your weight helps to reduce risk of lymphedema.
Manual Drainage techniques :Manual drainage is the most effective technique to reduce lymphedema, there are many techniques available to manage lymphatic drainage, you want to make sure physical therapists are certified and experienced in manual drainage, not all therapists are expert in manual drainage. In manual drainage its proper sequence and protocol that need to be followed for best result.
Manual Drainage after cosmetic surgeries:
- Brazilian Butt Lift (BBL)
- Tummy Tuck/Abdominoplasty
- Liposuction
- Fat Transfer
- Arm/Leg Lift
- Facelift
- Breast Implant
- Chin Liposuction
- Mastectomy/Breast Reconstruction
Research: Below is a study done by the NIH (National Institutes of Health) showing the benefits of post liposuction MLD.
MLD After Cosmetic Surgeries
One of the side effects of cosmetic surgery is swelling. This is a typical inflammatory response and a stage in the healing process as fluid rushes to the area to provide it with white blood cells. Increased edema is a common side effect of body procedures, particularly liposuction and stomach tucks..(READ MORE)
Manual Lymph Drainage Vs Diuretics
Can a water pill treat my persistent swelling?
No. A water pill, also known as a diuretic, is frequently taken by a person before they are aware that they have chronic edema. Chronic edema won’t be reduced by water tablets. Instead, they might mask the illness to momentarily ease suffering. Most patients find that water pills gradually lose their effectiveness, at which point they start to consider alternative causes for their persistent edema.
I have persistent edema. I’ve been taking water pills; should I stop?
It differs. If you have an underlying medical issue, such as a heart condition or high blood pressure, diuretics may be continued. Also available are substitute medications. Patients should discuss this with their doctor before using water tablets to treat lymphedema or any other medical condition other than swelling.
Why are water tablets ineffective in the management and treatment of chronic swelling?
Although diuretics may reduce swelling, they can actually make it more difficult to treat in the long term. This is especially true for chronic swelling conditions like lymphedema, which have a lot of proteins in the lymph fluid.
Diuretics reduce the amount of water in the lymph, which causes the proteins to become more concentrated. In contrast, medications containing benzopyrone can help remove plasma proteins from the tissue, rather than just temporarily reducing edema fluid like diuretics. However, when plasma proteins are still present in the tissue, they can attract fluid back to the edematous area, causing the previously reduced swelling to return.
This can also lead to the formation of hardened tissue, known as fibrosis, which makes it difficult to drain the edema. Diuretics can obstruct lymph flow and ultimately make the swelling worse, especially in cases where the edema is highly fibrotic and has already undergone treatment.
Download Your Free Ebook On 5 Steps To Manage Lymphedema
What will you learn from the book?
- You will know best daily routine to follow up Self-massage techniques
- What wraps and bandages are best for you
- Steps for your routine skin care
Lymphatic Drainage Massage Frequently Asked Questions:
Lymph is a clear fluid contained in the lymph nodes that help filter proteins and waste, and metabolizes cells in the body.
The lymph nodes remove the waste and circulate clean lymph fluid through the body. Lymph nodes contain white blood cells called lymphocytes. There are between 600 and 700 lymph nodes in the body.
The lymphatic system is the system of the body that helps maintain fluid levels in the body, circulate lymph fluid, fight off infection, and help circulate blood.
The lymphatic system is a part of the healing process and helps remove toxins from the body under periods of stress.
At Sure Cure, we are certified in MAnual lymphatic drainage and scar Management,our physical and massage therapist help you achieve your goals, We follow Vodder’s manual lymph drainage techniques which is considered gold standard in Lymphatic drainage. We use Dolphin neurostim Microcurrent for scar management and enhance lymphatic restoration after ablation surgeries and cosmetic surgeries.
SYMPTOMS OF POOR LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE:
– Swelling in arms and legs
– Changes in the condition of the skin
– Changes in the skin color
– Blisters
– Fluid leaking
Here are the major symptoms of poor lymphatic drainage:
– Swelling in arms and legs
– Changes in the condition of the skin
– Changes in the skin colour
– Blisters
– Fluid leaking
Lymphatic drainage massage can be used to address a variety of conditions, including:
– Lymphedema
– Lipedema
– Edema
– Post-liposuction
– Tummy tuck
– Cosmetic surgery/procedure
– Mastectomy
– Brazilian butt lift (BBL)
– Mommy makeover
– Rheumatoid arthritis
– Fibromyalgia
– Joint replacement
– Preeclampsia during pregnancy
– Postoperative swelling and discomfort
– Muscle aches and pains
