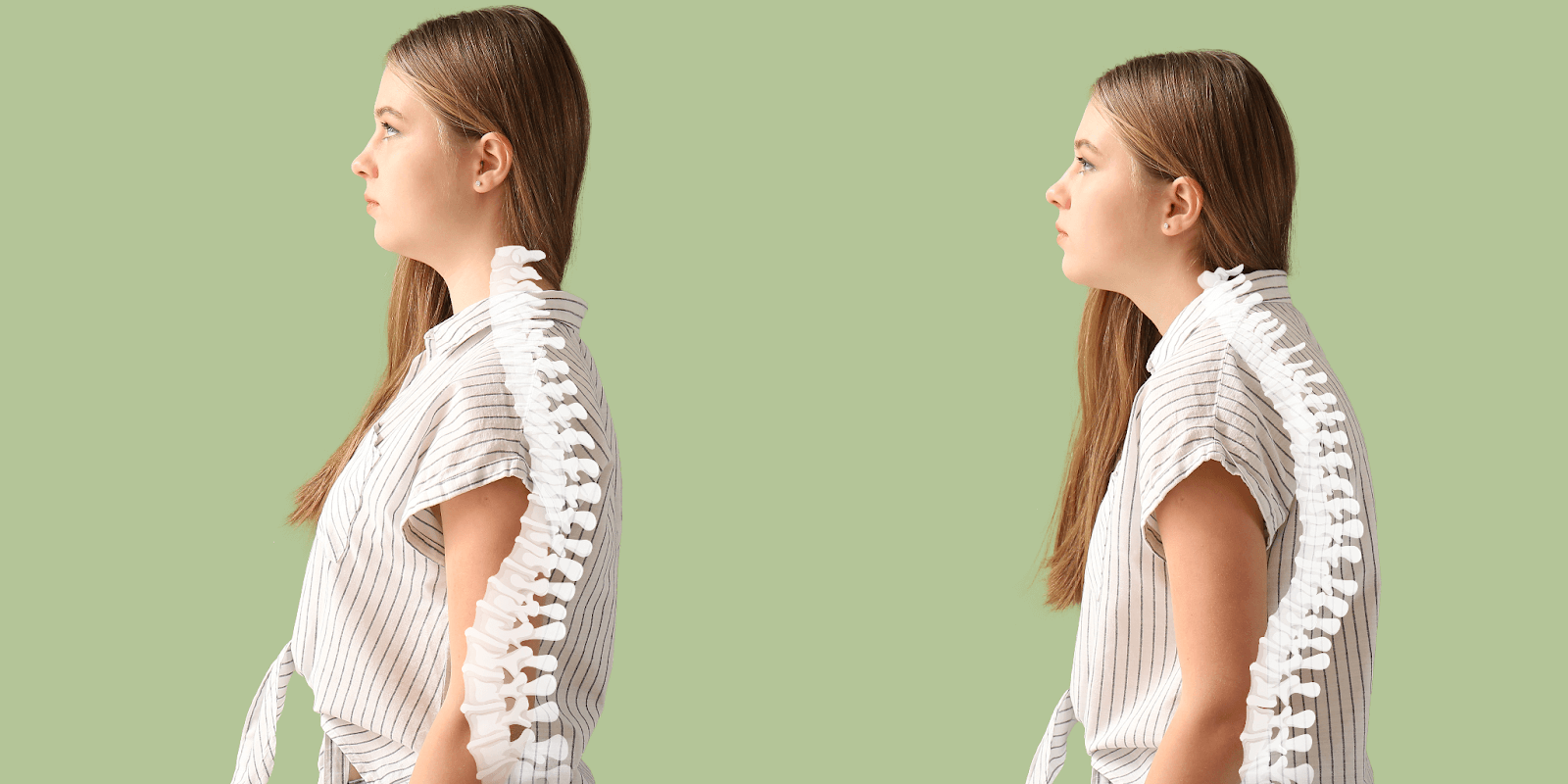
Many people, including our esteemed patients at Sure Cure, undervalue the importance of proper posture and all of its advantages for leading a healthier lifestyle, as we have seen.
People frequently find themselves spending lengthy hours commuting, standing for extended amounts of time, moving heavy objects, taking care of children, sitting at workstations, or engaging in leisure activities like binge-watching TV shows in today’s fast-paced environment. On the other hand, bad posture during these routine tasks might have a long-term negative impact on your lifestyle and health.
Learn vital information about posture, its significance, and useful hints to protect yourself against the possibility of aging-related neck, shoulder, and back problems. The purpose of this educational blog article is to arm you with the knowledge necessary to make wise decisions regarding your posture and general health.
Understanding Posture
The way your body is positioned when you sit, stand, or lie down is called your posture.
Good posture is about maintaining relaxed muscles and joints, not only about how you look.
An optimally positioned body facilitates optimal blood and oxygen circulation, which lowers the likelihood of developing subsequent joint and muscle issues.
The Importance of Good Posture
Maintaining proper posture is critical to general health. Proper posture when standing or sitting benefits not only your back but also your blood vessels, muscles, ligaments, and tendons.
Individuals with good posture, whether standing or sitting, are less likely to experience neck and back pain. Ignoring this pain could result in more significant issues like sciatica.
Learning how to move, lift, sit, and sleep with proper posture will help your body to do these activities without overstressing its muscles and ligaments.
How Bad Posture Affects Your Health
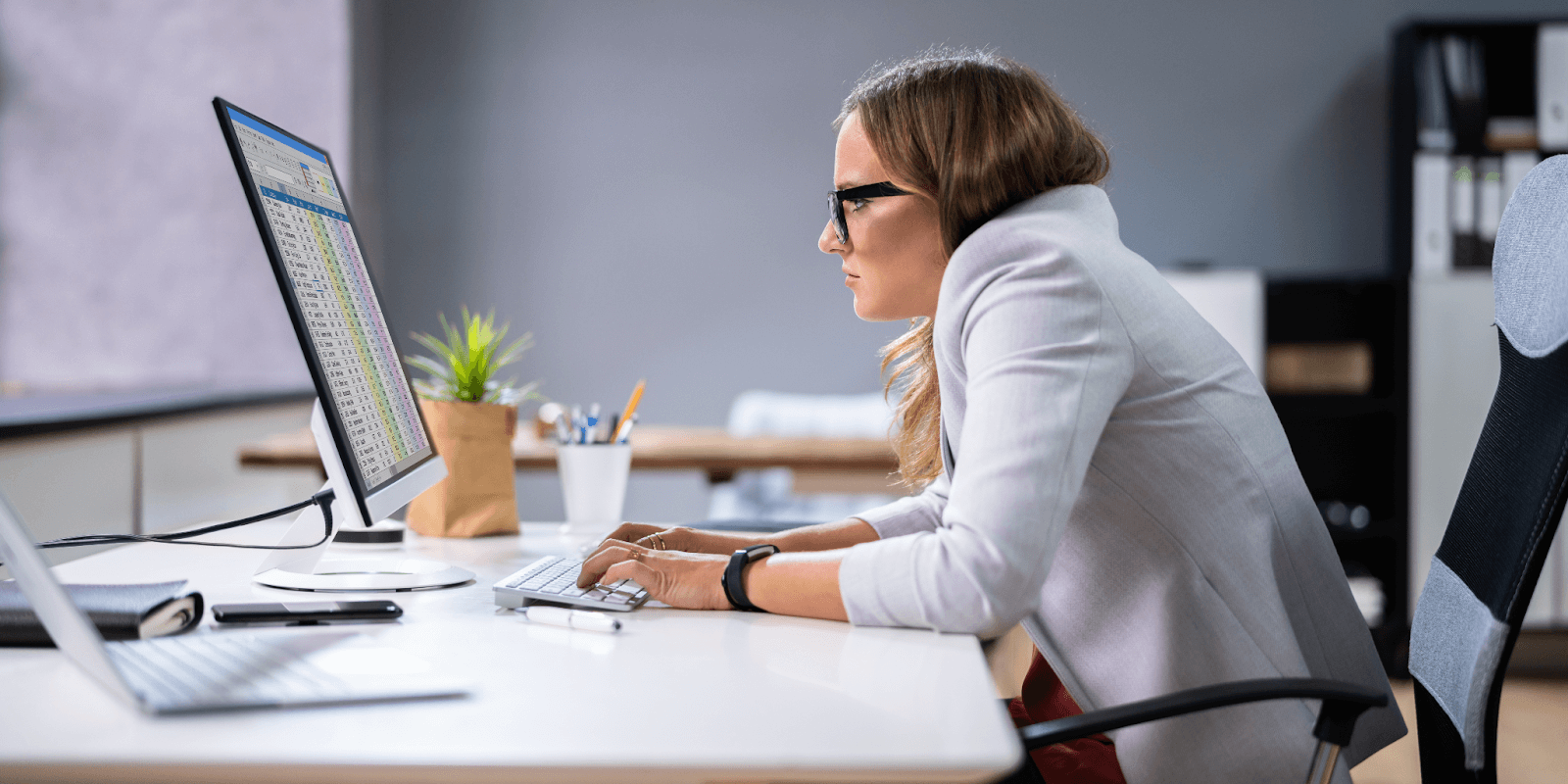

Many individuals are unaware that poor posture can disrupt blood flow, which leaves your lungs deficient in oxygen and leaves you feeling exhausted all the time. It may also result in persistent pain in your shoulders, back, and neck.
Ignoring the need to correct your posture can have serious consequences in the future. Ill posture can lead to more serious conditions like sciatica, slipped disks, and overall body misalignment.
Furthermore, these problems are not localized; they can also significantly complicate routine, everyday work. Find out why maintaining proper posture is crucial to maintaining your general health and wellbeing.
What Steps Can I Take to Improve My Posture?
We’re happy that using the advice in this blog, you’re interested in being healthier! Try out the tips we provided to improve your posture. Although following these suggestions won’t make you feel better right away, doing so will pay off in the long run.
These are practices that are essential for everyone seeking a higher standard of living. Take a look at these useful suggestions to help you live a more pain-free and pleasant future.
Our Top Tips to Improve Your Posture and Prevent Back Pain:
- Sit Up Straight

Even though it seems like common sense, a lot of people neglect to protect their backs while they sit. Make sure your chair is adjusted to adequately support your back if you work in an office. Use your chair to its full potential—it’s there to support you!
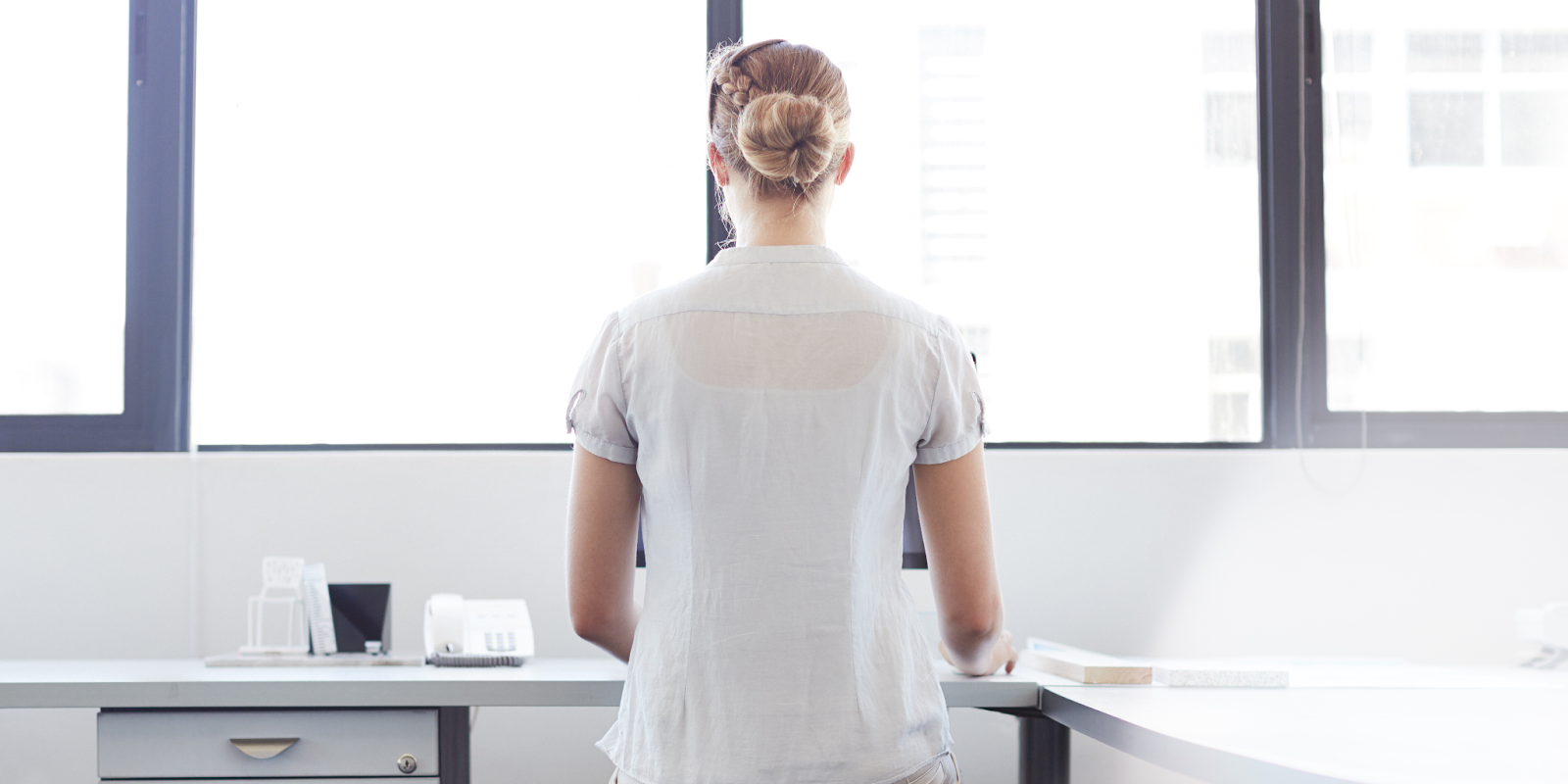
- Stand Up Straight
 Try to stand up straight if you are on your feet a lot. Refrain from giving in to the need to relieve your weight on one leg. To keep your posture straight and feel more at ease while standing, distribute your body weight equally between your two legs.
Try to stand up straight if you are on your feet a lot. Refrain from giving in to the need to relieve your weight on one leg. To keep your posture straight and feel more at ease while standing, distribute your body weight equally between your two legs. - Move Around Regularly:
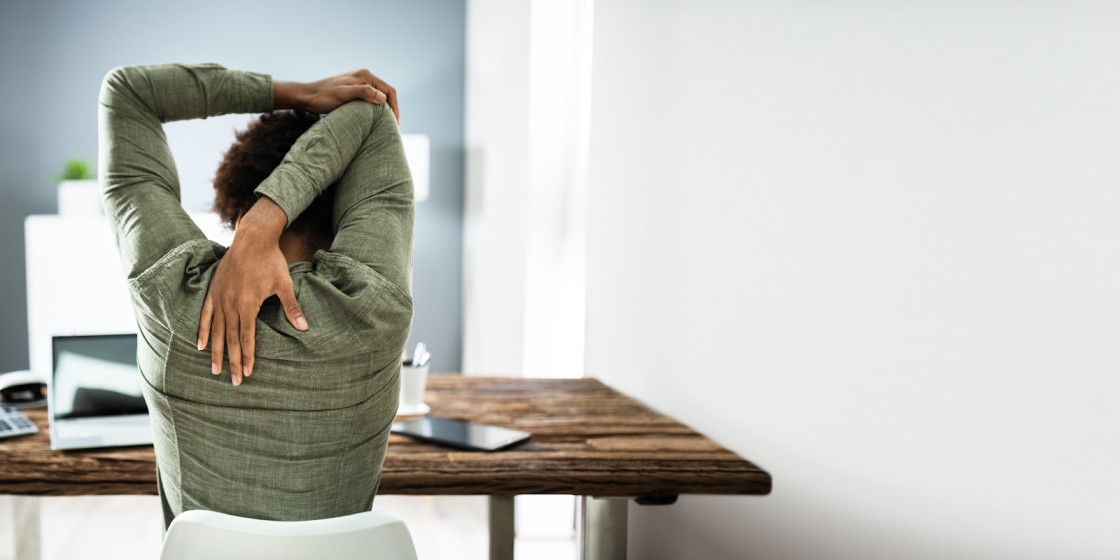 Take breaks to move about in order to avoid slouching and discomfort. Every thirty minutes, take a quick walk, stand up, or stretch. Think of it as a revitalizing respite for your body. By sticking to this pattern, you’ll feel refreshed and prepared to resume your work or carry on with your day.For long-term wellbeing, keep moving and progressively include regular exercise into your schedule.
Take breaks to move about in order to avoid slouching and discomfort. Every thirty minutes, take a quick walk, stand up, or stretch. Think of it as a revitalizing respite for your body. By sticking to this pattern, you’ll feel refreshed and prepared to resume your work or carry on with your day.For long-term wellbeing, keep moving and progressively include regular exercise into your schedule.